Data Networking Fundamentals
Data networks are used as local and wide area networks for everything from office computer networks to large scale telecommunications networks.
Data Networking Fundamentals Includes:
Networking fundamentals
Local area networks
Wide area networks
See also:
Software defined networks
Network functions virtualisation
SD-WAN
Data networks and data networking technology touches every area of modern life either directly or indirectly.
Data networks are used for local area networks within offices and businesses; networks are used for home computer systems and normally incorporate Wi-Fi to enable a host of devices to be connected; they are used for telecommunications applications providing connection for landline and mobile telecommunications; . . . and they are used in almost every walk of life.
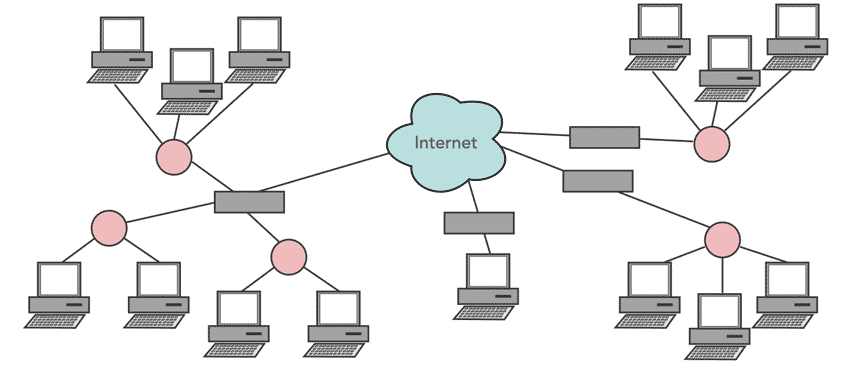
Although the various data networks used for different scenarios are different, there are some fundamentals that are common across the the data networking industry. Data is being passed from one point to another, and the basic concepts are the same whatever the application.
Not only are the basic building blocks the same, although the scale may be different, but many of the same issues present themselves in networks large and small - network security being but one example.
As data networking is is so important, the technology is moving forwards all the time. New techniques are being developed and the hardware is always improving and aspects like network security and network monitoring are also moving forwards apace to ensure that there is a safe and effective environment within the network.
Advantages of using networks
Data networks are used in a huge number of places and they form the cornerstone of today's data communications upon which the world relies very heavily these days.
As data networks are now commonplace, their advantages are often taken for granted. There are many advantages for setting up a data network:
- Shared resources: One very important aspect of the use of data networks is the fact that resources can be shared. Originally if a printer needed to be shared, for example, it would have to be disconnected from one computer and connected to another. Nowadays many resources are shared including printers, storage, even access to the Internet which will need a good firewall.
- Communication: When linked via a data network, communication is made very much easier. It is possible to send emails internally as well as externally, files can be transferred very easily, and there are many other ways in which linking computers via a network is beneficial. Without a network it was necessary to physically walk a floppy disc to the location where the file was needed (flash memory sticks were not invented then).
- Collaborative working: Using a data network it is possible to collaborate on working on a single document
- Access to centrally stored software it is often necessary to have a single copy of software stored on a central resource which can be accessed as required. When a licence is required to be used, this can be allocated from a central resource to a given user.
- Access to a central database: Many sales companies and other organisations have a central database which can be accessed by the telephone sales people as required. Being a central resource, it can be accessed by any of the relevant people.
Fundamentally the advantages of data networks all hinge round various forms of communication and shared resources. These make the justification for using networks very compelling.
Circuit switched and packet switched data
There are two main ways in which signals, and in this case, data can be sent across a network:
Circuit switched: Circuit switched data was the first way in which data was sent across networks. Using this concept, when data or even an analogue signal required to be sent from one point to another, a wire would be effectively switched into place and the data sent across this circuit.
Whether the circuit was active, or whether there was a quiescent period, that circuit would be dedicated to a given transfer. As data is typically sent in bursts, it meant that a large amount of time was spent when there was no data passing over the circuit.
Packet switched: Packet switched data operates by placing the data into defined packets of data, typically with added source and destination addresses as well as some other overheads. Although more data has to be sent, the fact that the use of the line is far greater, means that there is a significant improvement in the usage of the line.
When a large number of users can all share the same resource, far less infrastructure is needed and this reflects in much lower costs - bring benefits to network operators and users alike.
IP addresses
One major element of computer networking technology these days is the use of IP addresses. These addresses define the destination for the packet of data and also its source. By knowing these addresses, the network is able to route the data correctly.
IP or Internet protocol addresses are universal across the Internet, providing the addresses that are needed to forward data across the network to the required destinations.
The IP addresses are contained within the packet header, the data packet structure also being being defined within the IP standards.
Initially a version of Internet Protocol known as IPv4 was used. This had the familiar IP addresses consisting of a set of four numbers between 1 and 254, separated by dots. As the number of IP addresses started to run short a new version of IP known as IPv6 was introduced giving, amongst other advantages a huge number of additional IP addresses.
Network hubs, switches and routers
The very first computer networks were created just by connecting computers together. However as data networks and networking technology has grown, it is not possible to just link computers together. data needs to be routed across a variety of routes between a huge number of different endpoints.
To achieve this, network entities called hubs, switches and routers are used..
The hubs, switches and routers used in data networks are all different, and although the terms are often used (incorrectly) to describe any one of these entities, they are actually quite different:
- Network hub: A network hub is the most basic of the main network elements. The network hub passes on all the data that is received on one port to all the others. Hubs were often used as a common connection point. However the drawback is that because they send all data out to all ports, congestion can arise. Accordingly they are not widely used these days.
- Network switch: Network switches are more intelligent than hubs and they are widely used within large networks. Network switches filter and forward data presenting the data to be forwarded onto only the required port.
- Network router: Routers are the most intelligent forms of network node used for connecting data. A router has significantly more intelligence than a switch. It forwards data packets between networks, often from one router to the next until it reaches its destination. When a data packet arrives from one network, the router reads the address information to determine the ultimate destination. Using information in its routing table or routing policy, it directs the packet to the next network.
Routers often also contain significant additional capability in terms of knowing where data packets are to be forwarded and in terms of translation of addresses, etc.
Note on the Ethernet routers switches & hubs:
Ethernet routers, switches and hubs are essential elements for computer data networks, enabling data to be managed and forwarded as required. Routers, switches and hubs are different, having different capabilities. Although they are more commonly used with Ethernet, they are also widely available, especially for large networks with other interfaces as well.
Read more about the Ethernet routers switches & hubs.
Classes of data network
There is a lot ot talk about different types of data network: local area networks or LANs, wide area networks or WANs and even metropolitan area networks and others as well.
It is often helpful to gauge the scale of a computer or data network and understand its purpose and much information can be gained from how it is referred to.
Metropolitan area network, MAN : The name for the Metropolitan area network has fallen into a little disuse as it is neither a local area network nor a wide area network, and it does not really have a clear cut definition. That said, it has been suggested in some quarters that it might be between 2 and 50km wide.
Essentially the terminology is useful to indicate a network that has grown beyond that of a local area network and requires additional resources and planning to maintain it. To maintain the speed of connection between the nodes, fibre optic connections will need to be used. These and other enhancements will be required to maintain performance for the larger size.
Wide area network, WAN: The wide are network terminology is still widely used and it has ben suggested that this type of network is likely to be grater than 50km in diameter. A wide area network will not only have a lot of resources connected to it, but it will also need to have a fast connections and be well planned.
The term local area network is probably the most widely used as it is possibly the best defined. Most companies will have a local area network on a single site.
Network architecture
The way in which a data network is designed and implemented has a significant impact on its performance. Although it may appear that routers and switches can be added as required, this is not the optimum method of building an effective network.
Often with company computer networks, additional areas are added and this can be accommodated relatively easily, it is always best to plan the network architecture to obtain the optimum performance.
Data network developments
As the requirements for large data networks increase with efficiency, reliability and flexibility needing to be always increased. New techniques have been introduced to meet the needs.
- Software defined networking, SDN : One of the key techniques that is being used to improve the performance of data networks is called software defined networking. Using this technique the network control and forwarding functions are separated and this enables the network to be reconfigured more easily to meet the needs of the moment. If network monitoring is undertaken and the results presented, then reconfiguration can be undertaken with a complete knowledge of the performance of the network.
Read more about . . . . software defined networking.
- Network functions virtualization, NFV : Along with many other areas that use processing, it is possible to use a set of processing hardware that is standard across the network and this can be configured to provide the required function. As usage changes, this can be reconfigured to provide a different function if required. In this way the data network can respond to the needs of the minute more easily and effectively.
Read more about . . . . network functions virtualization.
Network monitoring
Large data networks can be very complicated items. Predicting how they will work, and even knowing when there is an issue can be difficult. Often if a node or other item fails, then the system will automatically route data via another route.
Whilst this level of automation is good, it is not always easy to detect when there is an issue, although latency (the time for the data to travel) will increase and there are likely to be data bottlenecks.
To overcome these issues, large data network normally have sophisticated network monitors. These network monitors are normally embedded in the system. As a result these network monitors are able to look at the operation of the network and detect issues and often detect ways in which the network could be reconfigured to optimise its operation.
For large data networks, the presence of network monitors is absolutely essential if the reliable operation of the network is to be ensured.
Network security
As the use of computer technology enters more areas of life and its importance increases, so too do the risks. With hackers becoming ever more resourceful, the topic of network security is of great concern.
There are several aspects to network security from the telecommunications network security to various aspects of computer network security.
Computer network security is of particular interest to anyone running any form of computer network, be it for a home computer system, or for a small or large enterprise.
Whether we like it or not, computer networks affect all walks of our lives, from the telecommunications networks we use, to home computer networks, to other large data networks used by companies when we need to buy something. data networks are in all walks of life and although they are used for slightly different purposes, many of the fundamentals are exactly the same.
 Written by Ian Poole .
Written by Ian Poole .
Experienced electronics engineer and author.
Wireless & Wired Connectivity Topics:
Mobile Communications basics
2G GSM
3G UMTS
4G LTE
5G
Wi-Fi
Bluetooth
IEEE 802.15.4
DECT cordless phones
Networking fundamentals
What is the Cloud
Ethernet
Serial data
USB
LoRa
VoIP
SDN
NFV
SD-WAN
Return to Wireless & Wired Connectivity