IEEE 802.11ax Wi-Fi 6
IEEE 802.11ax also known as Wi-Fi 6 provides a significant improvement in performance over its predecessors with improved spectral efficiency faster speeds, etc . . .
WiFi IEEE 802.11 Types Includes:
Standards
802.11a
802.11b
802.11g
802.11n
802.11ac
802.11ad WiGig
802.11af White-Fi
802.11ah Sub GHz Wi-Fi
802.11ax Wi-Fi 6
802.11be Wi-Fi 7
802.11 topics:
Wi-Fi IEEE 802.11 basics
Standards
Wi-Fi Alliance generations
Security
Wi-Fi Bands
Router location & coverage
How to buy the best Wi-Fi router
IEEE 802.11ax also known as Wi-Fi 6 is a new standard in the IEEE 802.11 series for wireless LAN technology.
802.11ax has been designed to provide significant improvements over 802.11ac, especially in terms of deployment of WLANs in dense areas, as well as improvements i spectral efficiency and user access, and many other features.
In view of this, IEEE 802.11ax is seen as the successor to 802.11ac and can provide improvements in speed of up to a factor of four.
Another of the key issues that 802.11ax resolves is that of mutual interference between different access points. In some densely covered areas this issue significantly slowed down the wireless networks using previous WLAN variants. Solving this issue rather than just providing bearers for faster data rates often has a much greater effect on real throughput.

802.11ax and Wi-Fi 6
In recent years a new form of designation has been used for the different variants of the wireless LAN variants using numbers like Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 7 etc.
Using the standard numbers like IEEE 802.11ax is not the most user-friendly method of referring to the different generations or versions of the Wi-Fi standard.
As most people are very familiar with the concept of generations of technology as a result of the mobile communications: 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, etc, the Wi-Fi Alliance decided to adopt a similar approach for the different variants of wireless LAN defined under IEEE 802.11.
The scheme adopted by the Wi-Fi Alliance refers to 802.11ax as Wi-Fi 6, 802.11ac as Wi-Fi 5 and 802.11n as Wi-Fi 4. No mention is made of previous versions of Wi-Fi.
Accordingly Wi-Fi 6 is the name given that now tends to be used as a marketing or sales name, rather than the more technical sounding standard variant. The new Wi-Fi Alliance designation are appearing on many Wi-Fi enabled devices such as Wi-Fi 6 routers, repeaters, laptops, tablets, phones, TVs and many more devices.
IEEE 802.11ax basics
IEEE 802.11ax is the next enhancement to the 802.11 Wi-Fi series beyond 802.11ac. The maximum data rate of "ac" is 7Gbps for a Wave 2 device and the maximum data rate for "ax" is 10 Gbps and this my be seen as only a small increase for the next generation of Wi-Fi.
However, the aim of IEEE 802.11ax is not just the headline speed, but a much better experience for users in all all environments, especially where there are high user density levels on a wireless LAN. Here previous generations often struggled and in places like airports, large offices, events and the like, Wi-Fi could be very slow when large numbers of devices were connected.
IEEE 802.11ax, Wi-Fi 6 seeks to resolve these issues and provide a much better level of service for large numbers of users of wireless networks.
Some of the key performance indicators for 802.11ax are the average per station throughput, area throughput, and also the power efficiency - and a number of capabilities have been introduced to improve the power efficiency for this version of Wi-Fi.
In terms of the headline specifications and parameters, a table of some of the key figures is given below.
| Summary of IEEE 802.11ax, Wi-Fi 6 Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Parameter | Details |
| Frequency bands | 2.4 GHz and 5GHz 6 GHz for Wi-Fi 6E as spectrum is allocated globally |
| Bandwidths | 20, 40, 80 MHz, & optional: 160 MHz, 80+80MHz |
| Modulation types | BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM, 1024QAM |
| FFT Sizes | 256, 512, 1024, 2048 Sub carrier space 78.125kHz |
| OFDM Duration | 12.8µs + 0.8 / 1.6 / 3.2 µs CP |
| Multi-user technology | OFDMA + MU-MIMO (UL + DL) with up to 8 spatial streams |
| Max data rate | 600.4 Mbps ( 80 MHz channel & 1 SS *) 9607.8 Mbps (160 MHz channel & 8SS *) |
Note: * SS = spatial stream.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access, OFDMA
IEEE 802.11ax, Wi-Fi 6 uses OFDMA, a technology which has been widely used in both the 4G and 5G mobile telecommunications systems.
The basic technology is based upon OFDM, orthogonal frequency division multiplex, where the data speed is slowed down to overcome reflections and multi-path propagation by spreading it over a number of very close spaced low data rate channels. This makes very good use of the available spectrum.
OFDM has proved itself to be resilient to reflections, selective frequency fading and interference, especially narrow band interference. It also provides a high level of spectrum usage efficiency.
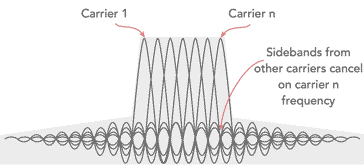
Note on OFDM:
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex, OFDM is a form of signal format that uses a large number of close spaced carriers that are each modulated with low rate data stream. The close spaced signals would normally be expected to interfere with each other, but by making the signals orthogonal to each other there is no mutual interference. The data to be transmitted is shared across all the carriers and this provides resilience against selective fading from multi-path effects.
Read more about OFDM, Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing.
The use of OFDMA with 802.11ax increases the capacity of the system by segmenting the channels into smaller sub-channels that overlap in frequency. Previous generations of Wi-Fi would wait until there was an available slot for the whole channel, but 802.11ax enables different devices to use sections of the channel, i.e. a number of the individual OFDM carriers and this enables simultaneous parallel transmissions to occur. In turn this makes the Wi-Fi network become more efficient because devices do not have to compete with each other for a time slot for the whole channel.
A further advantage of using OFDMA is that the Wi-Fi routers can dynamically adjust the power for each device, giving more power to more distant devices and less to those closer in.
In the uplink the 802.11ax router can group transmissions from multiple devices together and this can provide a sixfold increase in speed over existing networks.
The use of OFDMA in both uplink and downlink considerably improves the performance of the the WLAN for addressing multiple devices. With many more connected devices being used for remote control, etc around the home and office, these capabilities are needed.
Wi-Fi 6 MU-MIMO
802.11ax gives considerable improvements to the MIMO capabilities of the standard when compared to Wi-Fi 5, 802.11ac. Using MIMO, it is possible to improve the overall capacity considerably, whilst also being able to deliver better service to individual nodes.
MIMO or multiple input multiple output is a technique where the multiple transmissions paths present on any wireless communications link are used to advantage to improve the signal to noise ratio of the link, the data capacity or both.
Note on MIMO:
MIMO is a form of antenna technology that uses multiple antennas to enable signals travelling via different paths as a result of reflections, etc., to be separated and their capability used to improve the data throughput and / or the signal to noise ratio, thereby improving system performance.
Read more about MIMO technology
Multi-user MIMO, MU-MIMO is supported in both the up-link and down-link to provide additional performance
Modulation formats for 802.11ax
Even within the waveform format of OFDMA, a variety of different types of modulation can be used. The different modulation formats have different advantages, ones like BPSK provide a low throughput of data, but have a high resilience to noise, whereas formats like 256QAM have a much higher data throughput but can only be used when noise levels are low.
802.11ax has been designed to utilise BPSK right up to 1024QAM dependent upon the link conditions.
To achieve the maximum throughput for any given link, the system can alter the coding rate, error correction and the guard interval. The maximum data rate will also depend upon the channel bandwidth, and the number of spatial streams available.
There are several different defined sets of modulation coding schemes that are used for any system and 802.11ax is no different. They range from MCS0 using BPSK and providing the lowest data throughput for difficult link conditions to MCS 11 using 1024-QAM providing the highest data throughput, for instances when the link is particularly strong and robust in itself .
The modulation coding schemes used for 802.11ax enable the right level of modulation and coding to be set up for the prevailing conditions in the wireless communications like.
Selecting the right level of coding is key for the optimal operation of the wireless network.
Frequency bands
The first phase of 802.11ax knowns as Wi-Fi 6 was aimed at utilising the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands, although the standard itself was not band dependent. Products using these bands started to be introduced around 2020.
However additional spectrum is to be released around the globe at 6 GHz. This obviously provides more spectrum for use by Wi-Fi, and with this, better performance can be expected.
To differentiate the products that can only access the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands from the new ones that will be able to access 6 GHz as well, the Wi-Fi Alliance who have developed the terminology of Wi-Fi 6, etc and who promote Wi-Fi have coined the term Wi-Fi 6E, indicating that it has been extended.
The use of additional and wider channels in the 6 GHz portion of spectrum enables much better operation of the wireless LAN when compared to just using 2.4 and 5 GHz.
Spectral masks for the transmitters
In order that the transmitters within an access point or node do not cause interference to users on other channels, a spectral mask is defined giving the points on the spectrum for the signal. This ensures that the bandwidth does not fall outside the limits that give acceptably low levels of interference.
Different points and the spectrum for the signal are used and these must fall within the required bandwidth levels.
A scheme of frequency offsets from the centre is used.

| Channel Size (HMz) | A (MHz) | B (MHz) | C (MHz | D (MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 9.75 | 10.25 | 20 | 30 |
| 40 | 19.5 | 20.5 | 40 | 60 |
| 80 | 39.5 | 40.5 | 80 | 120 |
| 160 | 79.5 | 80.5 | 160 | 240 |
In the case of non-contiguous channels, as in the case of 80 + 80, then the 80 MHz mask is used for each 80 MHz signal.
These limits are used to test the transmitter output during the RF design stages of the electronic circuitry. If the transmission reliably falls within these limits during the RF design of the unit, then they should be correct during production.
The test limits are set understanding it is not possible to complete the RF design so that there is a perfect spectral mask. Some interference will always be present and spread onto other channels, but the limits have been set to ensure there is no undue interference and difference devices can operate together satisfactorily.
BSS colouring
One of the areas which 802.11ax is aimed at addressing is providing much higher levels of performance in areas where multiple Wi-Fi access points are operating - in airports, shopping malls, offices and the like.
One of the issues with operating multiple Wi-FI access points in relatively close proximity is that the different Wi-Fi access points cause interference to each other.
802.11ax uses a technique called BSS colouring to enable multiple Wi-Fi access points to operate on the same channel and it intelligently decides whether they can transmit at the same time. Using spatial re-use technology, the access point has a unique identifier of "colour".
With the previous versions of Wi-Fi, i.e. 802.11ac, Wi-Fi 5 and before, the WiFi devices listen for other signals before sending data. If a signal is heard, they wait for a random amount of time before retrying. This scheme is called Carrier Sense Multiple Access, CSMA. This means that when multiple Wi-Fi access points are operating on the same channel, the data throughput is considerably reduced.
For 802.11ax, the system is more intelligent. When an 802.11ax 6 router or device checks the channel and hears another signal, it will check the strength and its BSS Colour to determine if the signal is from a Wi-Fi access point on the same network. If it is not on the same network, it will decide whether it can transmit at the same time without causing any undue interference. In this way a Wi-Fi 6 router is able to share a channel with other Wi-Fi networks.
The 802.11ax standard provides for two different scenarios:
- Optimised for dense managed networks using planned Wi-Fi access points.
- Optimised for dense non-managed areas like cities where routers from several networks can interfere.
By setting up the two different scenarios and adjusting the mode of operation slightly, the Wi-Fi network is able to accommodate the different arrangements more effectively.
Target Wake Time
One of the issues with the use of Wi-Fi on mobile devices is that it can be a significant drain on the battery.To help overcome this issue, 802.11ax implements a feature called Target Wake Time. This allows the Wi-Fi radio in battery powered devices to enter a sleep mode when they are not exchanging data.
Using this technique, the 802.11ax, Wi-Fi 6 routers and devices can negotiate sleep cycles dependent upon the traffic and in this way they wake when it is their turn to communicate with the router. In this way, significant savings in power consumption can be made. In some circumstances the battery drain can be reduced by a factor of seven.
IEEE 802.11ax Wi-Fi 6 is a major enhancement for Wi-Fi technology. Although it will provide improvements for low usage applications, it will give significant improvements in dense areas where there are many users and Wi-Fi access points. With the release of additional spectrum at 6GHz, this will give further enhancements as the additional bandwidth will provide more capacity.
 Written by Ian Poole .
Written by Ian Poole .
Experienced electronics engineer and author.
Wireless & Wired Connectivity Topics:
Mobile Communications basics
2G GSM
3G UMTS
4G LTE
5G
Wi-Fi
Bluetooth
IEEE 802.15.4
DECT cordless phones
Networking fundamentals
What is the Cloud
Ethernet
Serial data
USB
LoRa
VoIP
SDN
NFV
SD-WAN
Return to Wireless & Wired Connectivity



