What is Carrier Ethernet - the basics
Carrier Ethernet basics - an Ethernet system that is used by carriers or service providers for high speed links for point to point links, LANs, mobile backhaul, etc. .
Ethernet IEEE 802.3 Includes:
Ethernet introduction
Standards
Ethernet data frame structure
100Mbps Fast Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet, 1GE
10 Gigabit Ethernet, 10GE
Single Pair Ethernet, SPE
Ethernet cables
How to buy Ethernet cables
How long can an Ethernet cable be
Routers, hubs, switches - the differences
Ethernet switch
How to buy best Ethernet switch
Ethernet industrial switch
Power over Ethernet, PoE
Ethernet splitter
Carrier Ethernet
Ethernet Products Shopping Page
Carrier Ethernet is a term that is used to describe Ethernet communications links that enable telecommunications network providers to provide Ethernet services to utilise Ethernet technology in their networks.
Typically Carrier Ethernet is used to provide point to point data links, links between local area networks, backhaul for mobile communications base stations and many other applications.
Traditionally the terms Metro Ethernet and Carrier Ethernet have been used interchangeably, but now Carrier Ethernet is normally the term that is used to signify a system that has additional facilities, and greater reliability, although in some areas there still might be distinctions between two implementations.
Carrier Ethernet development
Ethernet has been available for many years and has become the protocol of preference for local area networks for business and home. It is also widely used for direct links between various computer nodes.
Ethernet provides both speed and low level of cost because of its wide deployment and in addition to this, the Ethernet protocol is straightforward and easy to use, and its use is easily scaleable. As a result, it has become the standard of choice for most computer networking applications.
With business local area network requirements increasing and requiring different business LANs of different sites to be connected, as well as other areas like mobile backhaul needing an effective communications protocol, the concept of first Metro Ethernet and then Carrier Ethernet arose.
In order to promote and coordinate the technology and the relevant standards for carrier and Metro Ethernet, the Metro Ethernet Forum, MEF was set up in 2001.
This industry body has over 200 members of companies associated associated with the Carrier and Metro Ethernet industries as service providers, manufacturers, developers and the like.
What is Carrier Ethernet - definition
The Metro Ethernet Forum has set out a definition of what carrier Ethernet is.
Carrier Ethernet definition:
The MEF has defined Carrier Ethernet as a ubiquitous, standardized, carrier-class service and network with five attributes that distinguish it from familiar LAN-based Ethernet. These attributes are standardized services, scalability, reliability, management and quality of service.
It is useful to have the Carrier Ethernet definition because it enables users of Ethernet to understand exactly what CE is when compared to basic Ethernet.
Why carrier Ethernet
The question may be asked about the reason for having Carrier Ethernet when there is a perfectly good technical standard to define the technical aspects of the Ethernet interface used.
The reason is that the Ethernet standard works very well and this is the reason why it has been adopted, but carriers or operators and their users need more than just a technical standard that defines the technical aspects.
For Carrier Ethernet, it is necessary to define other operational aspects as well. Users are not particularly concerned about the technical method that is used to carry the data. Instead they are far more concerned with the levels of performance that are achieved. These affect the way it can be used and aspects like reliability, latency, and the like are particularly important.
It is these aspects rather than the technical definitions of the bearer technology that differentiate Carrier Ethernet from the basic technical Ethernet standard.
Carrier Ethernet key attributes
In order to understand the benefits of using Carrier Ethernet, it is necessary to look at the five key attributes mentioned int he MEF definition.
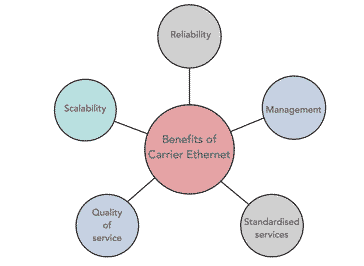
- Standardised services: One key advantage of Carrier Ethernet is that the services are standardised enabling easy implementation and interfacing wherever the user is located. The standardised include: Ethernet Private Line (E-Line), Ethernet Private LAN (E-LAN services), Ethernet Virtual Private Line and Ethernet Virtual Private LAN services. In view of the Carrier Ethernet standardisation, these Carrier Ethernet services can be delivered to the customer without the need for the customer to change the network or LAN equipment.
The MEF Certification Program for Carrier Ethernet services which are certified to conform to the MEF specification ensures the services conform to the five attributes specified. - Scalability: Businesses may not know what their future requirements will be and therefore a scalable delivery is required. The MEF standards specify that Carrier Ethernet services must be scalable to meet the needs of growing businesses.
- Reliability: A key requirement for any company is that any services must be reliable. Accordingly Carrier Ethernet services need to meet very stringent requirements for general quality, speed and availability. Carrier Ethernet networks must be able to monitor performance, detect incidents and recover from them without impacting performance. To achieve this, advanced network monitoring software is used along with redundancy to ensure that the service is not impacted when issues arise.
- Management: Service management is another key aspect of the requirements for Carrier Ethernet. Networks will typically use centrally accessible network monitoring and management software so that all aspects of the Ethernet network can be managed effectively from the main management office.
- Quality of service: The guarantee of end to end performance is what users require when using carrier Ethernet. Often users will be offered a variety of tiered options from which they can select the one that meets their requirements best. The service quality can include, voice, video or data or all three. Typically this is offered under the Service Level Agreement, SLA
These five key attributes separate Carrier Ethernet from other non-standard services that may be provided. By using Carrier Ethernet, it is possible to understand exactly what is being offered and know that the network services will interface easily, are expandable and will perform to the agreed level.
Carrier Ethernet services
There are two main types of Carrier Ethernet services that can be offered, but these categories can be split further as outline in the lists below:
- Ethernet Lines, E-Line: As the name indicates this form of Carrier Ethernet service provides a line that links two items together providing point to point connectivity. They may be use for providing Ethernet private line services, Ethernet-based Internet access services and point-to-point, P2P Ethernet VPNs.
- Ethernet Private Line, E-Line : A Carrier Ethernet private line consists of a point to point connection with a dedicated bandwidth as defined in the contact with the Carrier Ethernet supplier. The user's Ethernet frames are strictly separated from other users at the Ethernet layer, although the same physical lines may be used. In view of the fact that there is reserved bandwidth, the Ethernet Private Line has many similarities to legacy time division multiplex systems.
This type of line can be used to support a variety of requirements including Ethernet Internet, network services access or LAN to LAN interconnection. The Ethernet Private Line is the simplest of the Carrier Ethernet services to deploy. - Ethernet Virtual Private Line: In many respects a Carrier Ethernet virtual private line is very similar to that of a private line, providing point to point connectivity. The key difference is that instead of having dedicated bandwidth, the Virtual Private Line provides shared bandwidth.
The actual performance of the Ethernet Virtual Private Line will depend upon the agreement with the provider, but key network services and network parameters will often be defined: latency, minimum bandwidth, etc.
- Ethernet Private Line, E-Line : A Carrier Ethernet private line consists of a point to point connection with a dedicated bandwidth as defined in the contact with the Carrier Ethernet supplier. The user's Ethernet frames are strictly separated from other users at the Ethernet layer, although the same physical lines may be used. In view of the fact that there is reserved bandwidth, the Ethernet Private Line has many similarities to legacy time division multiplex systems.
- Ethernet LAN, E-LAN: The other main type of Carrier Ethernet service that is defined by the Metro Ethernet Form is the Ethernet LAN. Ethernet LAN services are designed to provide multipoint-to-multipoint connectivity. They are designed for native Ethernet transparent LAN services, and multipoint Ethernet VPNs.
- Ethernet Private LAN: Another common offering for Carrier Ethernet systems is an Ethernet Private LAN, EPLAN. This is effectively the Local Area Network equivalent of the Ethernet Private Line, but it provides multipoint connectivity and offers network services of dedicated bandwidth and it can connect two or more subscribers.
Often it is used to connect different sites together. Each of the customer sites is connected to a multipoint-to-multipoint Ethernet Virtual Circuit, EVC and using dedicated resources the different customers’ Ethernet frames are not multiplexed together. - Ethernet Virtual Private LAN: Carrier Ethernet is also used to provide Ethernet Virtual Private Line, EVPLAN services. These services may also be referred to as Virtual Private LAN Service, VPLS; Virtual Private Switched Network, VPSN; or a Transparent LAN Service, TLS.
This type of Carrier Ethernet service is a network service providing multipoint connectivity between Ethernet-edge devices. Being a virtual network, the resource is shared, and this means that care needs to be taken to ensure complete separation between different customers. This is achieved by encapsulation using VLAN tags or possibly MPLS.
As this service operates by sharing resources between multiple users it is very cost effective, but it can be complicated to operate because aspects like protection, bandwidth profiles, congestion management, buffering, etc., can be difficult to manage effectively.
- Ethernet Private LAN: Another common offering for Carrier Ethernet systems is an Ethernet Private LAN, EPLAN. This is effectively the Local Area Network equivalent of the Ethernet Private Line, but it provides multipoint connectivity and offers network services of dedicated bandwidth and it can connect two or more subscribers.
Carrier Ethernet is widely used for a variety of businesses that want a data link or a data network capable of providing a reliable level of service. As a result of its widespread use, there are many providers of equipment and services which ensures there is a good choice of services and prices remain competitive.
By defining the attributes of Carrier Ethernet, the Metro Ethernet Forum has been able to advance the use of Ethernet, because those needing it have a defined level of service and performance. It has also enabled the whole arena to expand as there is an open standard which can be used by all in a variety of different networking services areas.
 Written by Ian Poole .
Written by Ian Poole .
Experienced electronics engineer and author.
Wireless & Wired Connectivity Topics:
Mobile Communications basics
2G GSM
3G UMTS
4G LTE
5G
Wi-Fi
Bluetooth
IEEE 802.15.4
DECT cordless phones
Networking fundamentals
What is the Cloud
Ethernet
Serial data
USB
LoRa
VoIP
SDN
NFV
SD-WAN
Return to Wireless & Wired Connectivity