Transistor Circuits Collection
Browse through our collection of transistor circuits which give the circuits, design details, formulas for calculations as well as tips and guidelines for for the best operation.
Transistor Circuit Collection Include:
Transistor circuit collection
Common emitter
Emitter follower
Common base
Darlington pair
Sziklai pair
Current mirror
Long tailed pair
Constant current source
Capacitance multiplier
Two transistor amplifier
High pass filter
Switch circuits
Pulse generator
Schmitt trigger
One transistor relaxation oscillator
Transistor crystal-oscillator
How to run transistors in parallel
See also:
Transistor circuit design
The transistor enables many circuits to be designed with a variety of different functions. From amplifiers to buffers and filters to oscillators, current sources, long tailed pairs and many, many, more.
Whatever the circuit, the basic biasing conditions follow the same basic rules, but the topology of the circuit enables transistor to be used in a variety of ways to provide many different circuit functions.
Transistor circuits
There are many different types of transistor circuit. Each type has its own topology and fulfils a different function.
A selection of the different types of transistor circuit is given below:
- Common emitter transistor amplifier circuit: The common emitter amplifier is one of the most widely used types of transistor circuit. It is used in many applications where medium levels of input an output are acceptable and a medium voltage gain is needed. . . . . Read more about the Common emitter transistor amplifier
- Emitter follower transistor circuit: This type of transistor circuit is often used where a high input resistance and low output resistance is needed. It acts as a buffer circuit. It is also known as a common collector circuit. . . . . Read more about the Common collector / emitter follower transistor amplifier.
- Common base transistor circuit: The common base form of transistor circuit is not as widely used as the common emitter and emitter follower types. It does find applications in some microphone amplifiers and also for VHF / UHF RF amplifiers. . . . . Read more about the Common base transistor amplifier.
- Darlington pair: The Darlington pair is a form of transistor circuit configuration that is used to provide very high levels of gain. With the emitter of the first transistor connected to the base of the second, it effectively gives beta multiplication. This type f transistor circuit can be used in many ways and can give excellent performance. . . . . Read more about the Darlington pair.
- Sziklai pair: The Sziklai pair has many similarities to the Darlington, but using a slightly different configuration it can be used with a Darlington in transistor amplifier output stages. . . . . Read more about the Sziklai pair.
- Current mirror circuit: This type of transistor circuit is used widely within integrated circuits. It has two arms and the current flowing in one arm is mirrored by the other. . . . . Read more about the Current mirror circuit.
- Long tailed pair: The transistor long tailed pair circuit is a basic form of differential amplifier which forms the basis of many op-amp circuits. . . . . Read more about the Long tailed pair amplifier.
- Constant current source: Current sources are an important element in many designs, ensuring that a specific level of current is provided. There are different circuits giving basic to even temperature compensated performance. Read more about the Active constant current source.
- Capacitance multiplier: The transistor capacitance multiplier circuit has the effect of multiplying the effective capacitance of a capacitor by the value of β of a transistor. . . . . Read more about the Capacitance multiplier.
- Two transistor amplifier: A useful little circuit using a PNP and an NPN transistor providing a defined level of gain, with possibility for more gain that that provided by a single transistor. . . . . Read more about the Two transistor amplifier
- High pass filter: Even though operational amplifiers are capable of providing very good high pass filters, there is sometimes the need for a simple transistor circuit to provide the same function. . . . . Read more about the High pass filter.
- Transistor switch circuits: Understand the circuit design concepts behind using a transistor as a switch, and also discovering a number of options for using a transistor as a switch . . . . Read more about the Transistor switch circuits.
- Simple transistor pulse generator: There are occasions when a transistor pulse generator may be needed, generating a pulse of a reasonably defined with froma rising edge. These circuit provide an easy method of generating this from just a few electronic components . . . . Read more about the Transistor pulse generator.
- Schmitt trigger: The Schmitt trigger circuit can be implemented in a variety of ways using an operational amplifier, comparator IC, but it can also be implemented as a two transistor circuit. . . . . Read more about the Schmitt trigger circuit.
- One transistor relaxation oscillator: Although not an ideal choice for a new design project, this one transistor relaxation oscillator is good as a temporary hook-up circuit and it is exceedingly simple. . . . . Read more about the Simple one transistor relaxation oscillator.
Transistor circuits infographics
To give a quick overview of some of the more popular circuits I have created an infographic giving the basic details of the more popular transistor circuits.
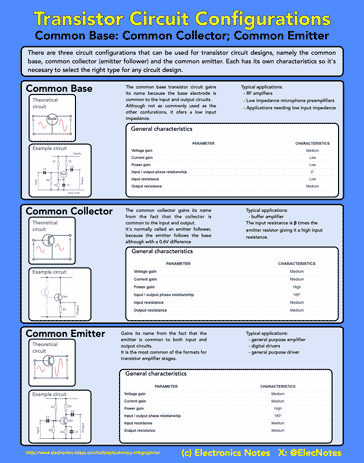
Click on image for larger version
This gives an outline of some of the different transistor circuit types. There is a vast number of different circuit types, each with its own function and parameters. Using these it is possible to build much larger circuits providing more complex overall function.
 Written by Ian Poole .
Written by Ian Poole .
Experienced electronics engineer and author.
Essential bipolar transistor data:-
Make your BJT transistor selection with op-amp data as well as distributor price and availability.
Check it out now!
More Circuits & Circuit Design:
Op Amp basics
Op Amp circuits
Power supply circuits
Transistor design
Transistor Darlington
Transistor circuits
FET circuits
Circuit symbols
Return to Circuit Design menu . . .



