What is a Super Capacitor, Supercap, or Ultracapacitor
The super capacitor or supercap is a useful form of very high value capacitor for use in applications like temporary supply hold-up.
Home » Electronic components » this page
Capacitor Tutorial Includes:
Capacitor uses
Capacitor types
Electrolytic capacitor
Ceramic capacitor
Ceramic vs electrolytic
Tantalum capacitor
Film capacitors
Silver mica capacitor
Super capacitor
Supercapacitor vs batteries
Surface mount capacitors
Specifications & parameters
How to buy capacitors - hints & tips
Capacitor codes & markings
Conversion table
A Concise Guide to The Basics of Capacitance
The super capacitor is a specialised form of capacitor that offers exceedingly high levels of capacitance – sometimes up to many farads.
Super capacitors may also be known as supercaps, ultracapacitors and some types are known as double-layer capacitors because of their structure.

Supercapacitor technology basics
The technology behind supercapacitors is different to that of an ordinary capacitor. It has to adopt a different approach to enable the ultra-high values of capacitance to be attained.
There are several types of supercap or ultracapacitor technology that can be used but the most widely adopted is known as the double-layer capacitor, DLC.
The DLC supercapacitor utilises a carbon-based technology that uses an organic electrolyte. This technology is easier to manufacture than the other types and therfore it has gained wider acceptance.
Like traditional capacitors, supercapacitors have two metal plates. These plates are coated with activated carbon which is a sponge-like porous material. These plates are immersed in an electrolyte which contains positive and negative ions. One carbon-coated plate, or electrode, is positive, and the other is negative. During charging, ions from the electrolyte accumulate on the surface of each carbon-coated plate.
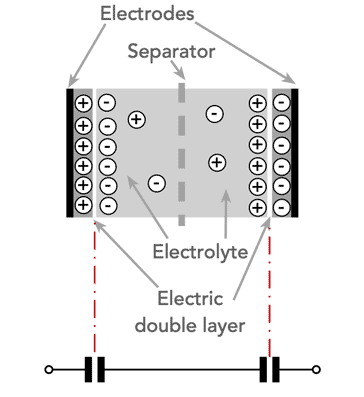
As charging occurs, the carbon electrodes have two layers of charge coating their surfaces and this gives rise to the name double layer capacitors. The distance between the two charge layers at the electrode is exceedingly small and this means that very high capacitance levels are achievable. Also as there are charge layers at each electrode, in effect a supercapacitor is actually two capacitors in series, one at each electrode
There are two types of double layer capacitor resulting from different charge storage mechanisms:
- Electrical double-layer capacitor: An EDLC stores energy in the double-layer at the electrode/electrolyte interface. In this type of capacitor, the electrode material used for the construction of the cell for the former is mainly carbon material.
- Electrochemical double layer capacitor or super/pseudo-capacitor : supercapacitor sustains a Faradic reaction between the electrode and the electrolyte in a suitable potential window. In this type of supercapacitor the electrode material consists of either transition metal oxides or mixtures of carbon and metal oxides/polymers
For both types of capacitor, the electrolytes can be either aqueous or non-aqueous depending on the mode of construction of capacitor cell.
It is for this reason for supercapacitors and double layer capacitors may be marketed separately using different names. Often the double layer capacitors do not have quite as high a capacitance level.
Super capacitor applications
The very high capacitance of super capacitors makes them ideal for a variety of different applications – most of which are associated with power supplies.
One of the major uses is within hold-up supplies for memories where they enable memories which may be dependent upon their supplies to retain the data even if power is removed.
They are also used within un-interruptible power supplies, UPS, where they are able to provide high levels of power for a short interval - sufficient to keep the equipment oeprating until the pwoer returns or a back-up supply starts..
Super capacitors are also starting to be used within vehicles to provide peak load enhancement capability for the power source. They are also being used in regenerative braking systems where they store the energy reclaimed during braking for later use.
Supercapacitor vs battery comparison
The supercapacitor and some battery technologies compete for some applications. It is worth taking a look at the comparison between a typical supercapacitor and a Lithium Ion high capacity battery technology used today. Lithium ion technology has been taken for the comparison because it is the highest density battery technology in widespread use today.
The comparisons made are only for approximate evaluation and any decision should be based on exact figure obtained from manufacturers for devices being considered because technology in both areas is advancing swiftly.
| Comparison between Super Capacitor and Lithium Ion Battery | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Supercapacitor | Lithium-ion |
| Cell voltage | 2.3 - 2.7V | 3.6V |
| Charge time | 1 - 10 seconds | 10 - 60 minutes |
| Lifetime (charge / discharge cycles) | ~1 million | 500 - 3000 |
| Specific energy (Wh/kg) | ~5 | 100 - 200 |
| Specific power (W/kg) | up to 10 000 | 1000 - 3000 |
| Output voltage maintenance | Poor | Good |
| Safety | Relatively safe when abused | Less safe and have been known to explode on rare occasions |
| Cost per Wh | ~ 20 units | ~1 unit |
| Service life | ~10 years | ~5 years |
| Operating temperature range | ~ -40 to +65°C | ~ 0 to +40°C |

Supercaps limitations
The supercapacitor or ultracapacitor is widely used for many applications and the components are available from many suppliers and distributors. However there are a few points that shoud be noted when considering to incorporate one in a new design:
- Maximum voltage: There is a maximum voltage for ultracapacitors. Other types of capacitor can be manufactured to operate at high voltages, but supercapacitors are generally restricted to operating voltages in the region of 2.5 - 2.7V. It is possible to manufacture them for operation above 2.8V but it is found that the operational life is reduced.
- Series operation: In order to achieve higher operating voltages for supercapacitors, they can be placed in series. This reduces the total capacitance as is the case with any capacitors placed in series. Also if more than three capacitors need to be placed in series then it is necessary to implement voltage balancing techniques. As the leakage currents through the capacitors are likely to be different, the voltage split across the capacitors will not be equal and one or more may enter and over-voltage position.
- Self-discharge: Self discharge of supercapacitors can be an issue in some circumstances. It results from the electrolyte used and it means that the energy stored can decrease by 50% or more within about a month or so. By comparison a nickel based battery (NiCd or NiMH) self-discharges by about 10% or more a month and a Li-ion battery by about 5% a month.
Generally, the limitations for supercaps are not a major issue. They can normally be overcome in those areas where they are an issue, and in some they may not cause any problem.
Super capacitor capacitor summary
The table below provides some of the salient features about some of the more widely used metal film capacitors that can be taken into consideration when designing circuits or replacing old components.
| Super Capacitor, Supercap Summary | |
|---|---|
| Parameter | Details |
| Value range | ~0.1 Farad upwards |
| Working voltage | Typically 2.5 – 2.8 V |
 Written by Ian Poole .
Written by Ian Poole .
Experienced electronics engineer and author.
More Electronic Components:
Batteries
Capacitors
Connectors
ADC
DAC
Diodes
FET
Inductors
Memory types
Phototransistor
Quartz crystals
Relays
Resistors
RF connectors
Switches
Surface mount technology
Thyristor
Transformers
Transistor
Unijunction
Valves / Tubes
Return to Components menu . . .



